Clearly identifying your brand as the sender of your messages has been a long-time best practice.
That’s because messages sent from unknown or unrecognized senders raise red flags for consumers, who may rightfully assume the message is spam or, worse, a phishing attempt.
Recently, Google and Yahoo added even more weight to this best practice, now requiring all brands that send more than 5K messages per day to send from a branded sending domain.
A branded sending domain is a type of sending domain, and a sending domain is where your emails appear to be sent from. There are two types:
- Shared sending domain
- Branded sending domain
If you use the Klaviyo shared sending domain, for instance, the klaviyomail.com domain appears in the sender information at the top of an email.

A shared sending domain is great for a sender that is just starting out and does not send more than 5K messages in a day.
But once you send 5K messages in a single day, you are known as a bulk sender—and Google and Yahoo now require you to send messages from the same root domain as your website.
Here’s an example. When Klaviyo sends emails, our root domain is the same as our website domain: klaviyo.com.

That means that Klaviyo is sending emails from a branded sending domain. This not only keeps Klaviyo in compliance with the new Google and Yahoo requirements, but also:
- Builds trust and brand recognition with our audience
- Helps our emails land in inboxes properly
- Encourages engagement with those messages
Here are 3 reasons why a branded domain has long been a best practice for email deliverability and brand building—and why you should set one up now.
1. Strengthen deliverability by owning your sender reputation
Connecting a branded sending domain allows you to build a sending reputation on your brand’s own domain.
On a shared sending domain, you share your reputation with all senders on that domain. Even if you follow all best practices, there’s no guarantee that the other senders sharing the sending domain are doing the same.
Why allow your great sending practices to be affected by someone else’s poor actions? Setting up and sending from a branded domain limits any negative impact to your domain reputation and your deliverability.
In other words, you are the only one that will send from your domain—and that gives you more control over your sender reputation and overall deliverability.
Get a deep dive into email deliverability: what it is, what affects it, best practices, and brand examples.
Read full story2. Build brand loyalty by clearly identifying yourself
Aligning your root domain simply means matching your website domain with your branded sending domain, and using a common root domain throughout your email.
This best practice addresses the need for your subscribers to trust that mail coming from you is in fact from your company. After all, do you trust an email from a company that sends from a personal, free email address like company@gmail.com?
Now, let’s talk domain, subdomain, and root domain. It’s common for businesses to use various subdomains. That’s fine, as long as your root domain is consistent.
In the examples below, “example.com” is the root domain across each of these domain categories:
- Website = www.example.com
- Friendly-from = example.com
- Branded sending domain = send.example.com
- Click tracking domain = click.example.com
As long as the root of the domain matches, you will have alignment in your messaging.
3. Build security by setting up DMARC
Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance, also known as DMARC, is a technical standard that helps protect email senders and recipients from advanced threats that can be the source of an email data breach.
DMARC is now also required for bulk senders under the new Google and Yahoo requirements. And to accomplish it, you need a branded sending domain.
Use the flowchart below to understand if and when you need to set up DMARC.
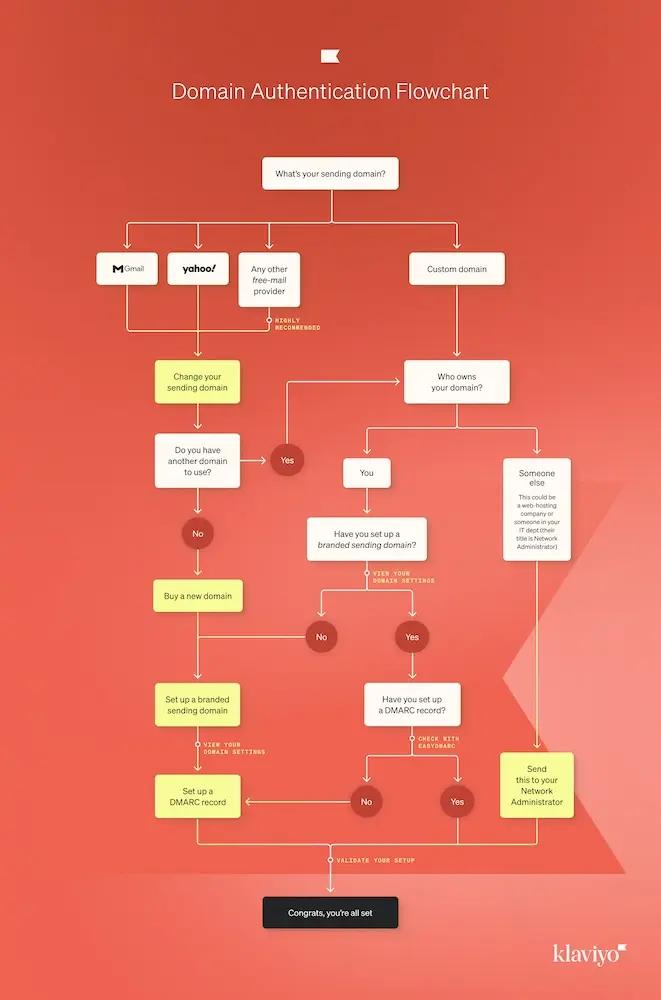
Ultimately, using a branded sending domain will lead to more consistent branding and early trust building with consumers, and will result in your messages landing in inboxes consistently.
And all of that equals more revenue from your email marketing efforts.
Power smarter digital relationships with Klaviyo SMS.
Get started